Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsions MS-2 Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make MS-2 an easy to use and a safe product. MS-2 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2 is recommended for Pre Mix Carpet and Patchwork. The application rate as per MoRTH is as below:

Packing of Bitumen Emulsion MS2
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion MS-2 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion MS2
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 25 °C, SFS | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve (%) | — | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 65 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | — | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make QS-1h an easy to use and a safe product. QS-1h can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Packing of Bitumen Emulsion QS1h
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion QS-1h is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion QS1h
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SSF , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Viscosity SSF , 50 °C (s) | ASTM D244 | ||
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | ASTM D6930 | ||
| Demulcibility , 0.02 N CaCl2 (%) | |||
| Cement mixing (%) | |||
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 57 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 40 | 90 | ASTM D5 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different braking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsions RS-2 Applications
Anionic Slow Setting bitumen emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make RS-2 an easy to use and a safe product. RS-2 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2 is recommended for Surface Dressing treatment and the application rate as per MoRTH is as below

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS2 Packing
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion RS-2 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Bitumen Emulsion RS2 Specifications
| Properties | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SFS , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | 1 | ASTM D6930 | |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Demulcibility , 35ml, 8% dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, % | 60 | — | ASTM D6936 |
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 63 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different braking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make RS-1 an easy to use and a safe product. RS-1 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
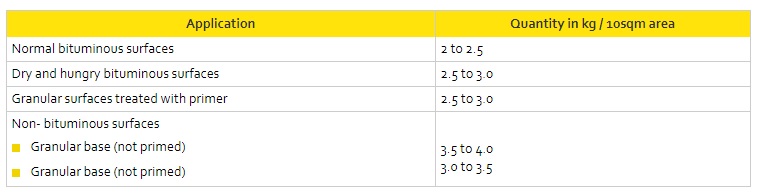
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 is recommended for Tack Coat treatment and the application rates as per MoRTH are as below:
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS1 Packing
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion RS-1 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Bitumen Emulsion RS1 Specification
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SSF , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Demulcibility , 35ml, 8% dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, % | 60 | — | ASTM D6936 |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve (%) | — | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 55 | — | ASTM D244 |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | — | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1h
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1h Description

Anionic Bitumen emulsion SS-1h is a slow-setting, anionic type and is further characterized by their ability to remain stable on storage although produced with equipment that generates a wide range of shearing forces. Such characteristics are imparted to the asphalt emulsions through the use of emulsion-conditioner compositions comprising a partially desulfonated lignosulfonate, preferably an anionic or nonionic emulsifying agent and, optionally, a thickener.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different braking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
An Anionic emulsion has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
Usage of anionic bitumen emulsion SS-1h is two phases of water and bitumen which are not possible to mix and the first interphase is inside of the outer phase. The particle size of the emulsion is 0.1 to 5 micron. In normal conditions and without emulsifier the two parts of emulsion SS1 are unstable and quickly will segregate. By adding emulsifier into water and bitumen that is the alkaline salt with Ammonium Salt in the high-speed mixer at ISO condition making bitumen SS-1h.
The percentage of emulsifiers is 3-5% and total water content is between 30-50%. By adding an Emulsifier to bitumen and water we put anionic electron on the material and each particle of bitumen became like a circle with a size of 0.001 to 0.01 mm and become floating in the water. Using bitumen SS1 is environmentally friendly since any flammable material or kerosene is not used and firing of the bitumen during the usage would be zero.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1h Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make SS-1h an easy to use and a safe product. SS-1h can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Anionic Bitumen emulsion SS1h Packing
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion SS-1h is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Bitumen Emulsion SS1h Specifications
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SSF , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Viscosity SSF , 50 °C (s) | — | — | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Demulcibility , 0.02 N CaCl2 (%) | |||
| Cement mixing (%) | 2 | ||
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 57 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 40 | 90 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1 Description

For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different braking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
An Anionic emulsion has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
Anionic Bitumen emulsion SS-1 is a slow-setting, anionic type and is further characterized by their ability to remain stable on storage although produced with equipment that generates a wide range of shearing forces. Such characteristics are imparted to the asphalt emulsions through the use of emulsion-conditioner compositions comprising a partially desulfonated lignosulfonate, preferably an anionic or nonionic emulsifying agent and, optionally, a thickener.
Usage of anionic bitumen emulsion SS-1 is two phases of water and bitumen which are not possible to mix and the first interphase is inside of the outer phase. The particle size of the emulsion is 0.1 to 5 micron. In normal conditions and without emulsifier the two parts of emulsion SS1 are unstable and quickly will segregate. By adding emulsifier into water and bitumen that is the alkaline salt with Ammonium Salt in the high-speed mixer at ISO condition making bitumen SS1.
The percentage of emulsifiers is 3-5% and total water content is between 30-50%. By adding an Emulsifier to bitumen and water we put anionic electron on the material and each particle of bitumen became like a circle with a size of 0.001 to 0.01 mm and become floating in the water. Using bitumen SS1 is environmentally friendly since any flammable material or kerosene is not used and firing of the bitumen during the usage would be zero.
This kind of anionic bitumen has more adhesive to building material which contains lime.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1 Applications
Anionic Slow Setting bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-liberated liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make SS-1 an easy to use and a safe product. SS-1 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
It is using for cold asphalt in cold or humid or sealing. Asphalt emulsions are widely used in highway construction, surfacing, and maintenance. They are also used in various other applications where water-repellent surfaces are needed. Slow-setting emulsions are grades of emulsions that are sufficiently stable to allow mixing with fine or dusty aggregate mineral particles and further processing before setting to a coherent mass. Such grades of asphalt emulsions (bitumen SS-1 grade), when anionic, react chemically with portland cement constituents forming a water-insoluble salt and thus possess valuable water-resistant characteristics.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1 Packing
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion SS-1 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Bitumen Anionic Emulsion SS-1 Specifications
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SSF , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Viscosity SSF , 50 °C (s) | — | — | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Demulcibility , 0.02 N CaCl2 (%) | — | — | |
| Cement mixing (%) | — | 2 | |
| Sieve (%) | — | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Residue (%) | 57 | — | ASTM-D244 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | ASTM D2042 | |
| Penetration 77°F (25°C) 100g,5s mm | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| ductility, 77°F (25 °C), 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion Description

Cationic Bitumen Emulsion is a stable dispersion of bitumen in water in the continuous phase. The bitumen globules are positively charged due to the NH3 + group cover which is formed around bitumen droplets and provides stability for emulsion by electrostatic repulsion. These bitumen droplets have an affinity with the negatively charged aggregate, which is usually available in India. Dispersion is obtained by processing bitumen & water-based solution under controlled conditions through a colloidal mill having a high-speed rotor in the presence of scientifically selected surfactants/emulsifiers. The selection of emulsifier & its quality is significant for emulsion stability, it’s breaking & curing when applied over aggregates. The Cationic Bitumen Emulsion is chocolate brown and free-flowing at normal temperature. Once it breaks the bitumen breaks out and color changes to black. An Emulsion is said to break when the organic and the aqueous phase separate into two distinct layers i.e. the dispersion ceases to exist. Emulsions are classified as Rapid Setting-1(RS-1), Rapid Setting-2(RS-2), Medium Setting (MS), Slow Setting-1 (SS-1), and Slow Setting-1 h (SS-1h). The breaking time varies according to the designation of Emulsion although being largely dependent upon the climatic condition i.e. temperature, humidity, wind velocity, etc.
The term cationic is derived from the migration of particles of bitumen under an electric field also. The droplets migrate toward the cathode (negative electrode), and hence the emulsion is called cationic. The cationic emulsifying agent functions similarly to the anionic; the negative portion of the head floats around in the water leaving a positively charged head. This imparts a positive charge to all the droplets. Since positives repel each other, all the droplets repel each other and remain as distinct bitumen drops in suspension. A typical cationic emulsifying agent is shown below showing the orientation of the agent at the bitumen-water interface and the positive charge imparted to each drop.
Cationic Emulsion Bitumen
| CRS | CMS | CSS |
| CRS-1 | CMS-2 | CSS-1 |
| CRS-2 | CMS-2h | CSS-1h |
Cationic type: In which the bitumen particles are positively charged and the emulsifier used is a long chain amine. These are suitable for use with siliceous aggregates like quartzite, sandstone, granite, etc.
When the emulsion is being produced the cations are adsorbed by bitumen droplets, negative ions remain in the water. The undeniably most complete field of use is represented by the rapid setting emulsions.
The choice of bitumen emulsion (i.e. whether anionic or cationic) to be used depends upon the mineral composition of aggregate used for construction. In the case of silica-rich aggregates, the surface of the aggregates is electronegatively charged. Therefore a cationic bitumen emulsion should be used. This will help better the spreading and binding of bitumen with aggregates.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion Description

HJ Oil Group is a supplier of high-quality Anionic Bitumen Emulsion.
The preparation of bitumen emulsion is essentially the grinding of bitumen in water with a surfactant. Therefore, the emulsifier is one of the most important components of bitumen emulsions, which directly influences the quality and characteristics of the product. The emulsifier is a surfactant. By chemical nature, surfactants are divided into several types, depending on the charge of its particles. Since water bitumen emulsions are used intensively as binding and film-forming material in construction, two types of emulsifiers are used: anionic and cationic.
Chemical surface-active agents, which serve as emulsifiers, are classified by the electrochemical charge that is attained when they dissociate in a water solution. In the case of anionic emulsions, the chemical charge is negative. The chemical type and quantity of surface-active agent used in the manufacturing process govern the process in which the resulting asphalt emulsion can be used.
The term Anionic Bitumen Emulsion is derived from the migration of particles of bitumen under an electric field. The droplets migrate toward the anode (positive electrode), and hence the emulsion is called anionic. In an anionic emulsion, there are “billions and billions” of bitumen droplets with the emulsifying agent at the water bitumen interface. The tail portion of the emulsifying agent aligns itself in the bitumen while the positive portion of the head floats around in the water leaving the rest of the head negatively charged and at the surface of the droplet. This imparts a negative charge to all the droplets. Since negatives repel each other, all the droplets repel each other and remain as distinct bitumen drops in suspension. A typical anionic emulsifying agent is shown below along with a diagram showing the orientation of the agent at the bitumen-water interface and the negative charge imparted to each drop.
ANIONIC EMULSION
| RS | MS | SS |
| RS-1 RS-2 | MS-1 MS-2 MS-2h HFMS-1 HFMS-2 HFMS-2h HFMS-2s | SS-1 SS-1h |
The difference is that the anionic bitumen emulsion is negatively charged, while the cationic emulsions are positively charged. The choice of emulsifier used in the preparation of the emulsions determines the efficiency and reliability of the product.
For certain reasons, cationic systems have a significant advantage over anionic emulsions. Most of the fillers used in road construction have a limited amount of positively charged particles, which can attract the negatively charged particles of the anionic emulsion. Therefore, it is more difficult to create a uniform structure and ensure a high degree of adhesion with an anionic surfactant. When using anionic emulsion, bitumen should be modified by additives, while in the cationic emulsion, the emulsifier itself serves as an adhesion additive.
Unlike cationic emulsions, which readily interact with alkaline and acidic minerals, anionic emulsions are less versatile and work well only with alkaline minerals.
The amount of emulsifier applied influences emulsion breakdown rate, i.e. the time until the bitumen precipitating from the emulsion, returns to its original state.
Cutback Bitumen SC-3000
Cutback Bitumen SC-3000 Description

Cutback bitumen SC-3000 is an asphalt cement that has a solvent or distillate such as gasoline, diesel fuel, kerosene, or naphtha added to make the asphalt liquid at ambient temperatures and improve its ability to coat aggregates. Two letters followed by a numerical digit designate or name a cutback asphalt.
Cutback asphalt can contain between 12 and 40 percent distillate. The high demand for the distillates to be used in energy applications and ever-increasing air quality regulations have caused a steady decline in the use of cutback asphalt.
The SC liquid asphalt may be obtained by fluxing an asphalt cement with a less volatile distillate such as gas oil. The SC-70 and SC-250 grade cutback asphalts are very similar to residual refinery products that are used as heavy fuel oils such as bunker C or Number six fuel oils. These SC cutback materials, whether straight run or fluxed with a relatively non-volatile material such as gas oil, are also known as “road oils”.
Cutback Bitumen SC-3000 Applications
Current common uses are in penetrating prime coats and in producing patching or stockpile mixtures. Cutback asphalt used in mixing with aggregate will usually contain an adhesion agent to assist in the coating of the aggregate surface.
Cutback agents are used to lowering the viscosity of bitumen when it is applied as a primer to the surface of a road pavement aggregate base course or substrate. Kerosene is used as a bitumen cutback agent at different concentrations according to local conditions and requirements.
The cutback bitumen is ideal for prime coat and cold applied because of easy uses and no need for thinning and heating.
Cutback bitumen SC-3000 consist of initial incorporation of asphalt into the surface of non-asphalt based course preparatory to any superimposed treatment of construction.
The cutback asphalt SC-3000 applying to waterproof of surfaces plug capillary voids, coat, and bond loose mineral particles.
Packing of cutback bitumen SC-3000
Packing of cutback bitumen SC-3000 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainers and tanker.
Safety of cutback Asphalt SC-3000
Refer to Safety Datasheets before use.
Transport, use, and store at the lowest temperature possible.
Eliminate all potential ignition sources during application.
Avoid breathing vapors. Avoid contact with skin.
Always wear appropriate PPE including heat protection when used hot.
DO NOT allow product or washings to enter stormwater or sewer systems.
Specification of Cutback Asphalt SC3000
We guaranty the quality of cutback SC-3000 with the arrangement of the international inspectors to check the quality and quantity of the bitumen on each shipment during the loading to vessel and controlling the production by the QC team via batch test report before shipping. RABIT guaranty the quality to meet with ASTM/EN 15322:2009.
| property | specification limit | specification limit | Test method |
| Min | Max | ||
| Kinematic viscosity at 60°C [140°F], mm2/s | 3000 | 6000 | ASTM D2170 |
| Flashpoint(Cleveland open cup), °C [°F] | 70 | — | ASTM D92 |
| distillate test | |||
| Total distillate to 360°C [680°F], volume % | — | 8 | ASTM D402 |
| Solubility, % | 95 | — | ASTM D2024 |
| Kinematic viscosity on distillation residue at 60°C [140°F], mm2/s | 2000 | 35000 | ASTM D2170 |
| Asphalt residue: | |||
| Residue of 100 penetration, % | 75 | — | ASTM D243 |
| Ductility of 100 penetration residue at 25°C [77°F], cm | 50 | — | ASTM D113 |
| Water, % | — | 0.5 | ASTM D95 |
Cutback Bitumen SC-800
Cutback Bitumen SC-800 Description

Cutback Bitumen SC-800 is an asphalt cement that has a solvent or distillate such as gasoline, diesel fuel, kerosene, or naphtha added to make the asphalt liquid at ambient temperatures and improve its ability to coat aggregates. Two letters followed by a numerical digit designate or name a cutback asphalt.
Cutback asphalt can contain between 12 and 40 percent distillate. The high demand for the distillates to be used in energy applications and ever-increasing air quality regulations have caused a steady decline in the use of cutback asphalt.
The SC liquid asphalt may be obtained by fluxing an asphalt cement with a less volatile distillate such as gas oil. The SC-70 and SC-250 grade cutback asphalts are very similar to residual refinery products that are used as heavy fuel oils such as bunker C or Number six fuel oils. These SC cutback materials, whether straight run or fluxed with a relatively non-volatile material such as gas oil, are also known as “road oils”.
Cutback Asphalt SC-800 Applications
Current common uses are in penetrating prime coats and in producing patching or stockpile mixtures. Cutback asphalt used in mixing with aggregate will usually contain an adhesion agent to assist in the coating of the aggregate surface.
Cutback agents are used to lowering the viscosity of bitumen when it is applied as a primer to the surface of a road pavement aggregate base course or substrate. Kerosene is used as a bitumen cutback agent at different concentrations according to local conditions and requirements.
The cutback bitumen is ideal for prime coat and cold applied because of easy uses and no need for thinning and heating.
Cutback bitumen SC-800 consist of initial incorporation of asphalt into the surface of non-asphalt based course preparatory to any superimposed treatment of construction.
The cutback bitumen SC-800 applying to waterproof of surfaces plug capillary voids, coat, and bond loose mineral particles.
Packing of Cutback Bitumen SC-800
This cutback bitumen bulk in the tanker and also in new steel and thick drum on the pallet to prevent all leak inside of the container.
Safety of Cutback Asphalt SC-800
Refer to Safety Datasheets before use.
Transport, use, and store at the lowest temperature possible.
Eliminate all potential ignition sources during application.
Avoid breathing vapors. Avoid contact with skin.
Always wear appropriate PPE including heat protection when used hot.
DO NOT allow product or washings to enter stormwater or sewer systems.
Specification of Cutback Asphalt SC800
We guaranty the quality of cutback SC-800 with the arrangement of the international inspectors to check the quality and quantity of the bitumen on each shipment during the loading to vessel and controlling the production by the QC team via batch test report before shipping. RABIT guaranty the quality to meet with ASTM/EN 15322:2009.
| Property | Specification limit | Specification limit | Test Method |
| Min | Max | ||
| Kinematic viscosity at 60°C [140°F], mm2/s | 800 | 1600 | ASTM D2170 |
| Flashpoint(Cleveland open cup), °C [°F] | 70 | — | ASTM D92 |
| Distillate test | |||
| Total distillate to 360°C [680°F], volume % | — | 15 | ASTM D402 |
| Solubility, % | 95 | — | ASTM D2024 |
| Kinematic viscosity on distillation residue at 60°C [140°F], mm2/s | 1000 | 16000 | ASTM D2170 |
| Asphalt residue: | |||
| Residue of 100 penetration, % | 60 | — | ASTM D243 |
| Ductility of 100 penetration residue at 25°C [77°F], cm | 50 | — | ASTM D113 |
| Water, % | — | 0.5 | ASTM D95 |
