Caustic Soda Flake
Caustic Soda Flake Description
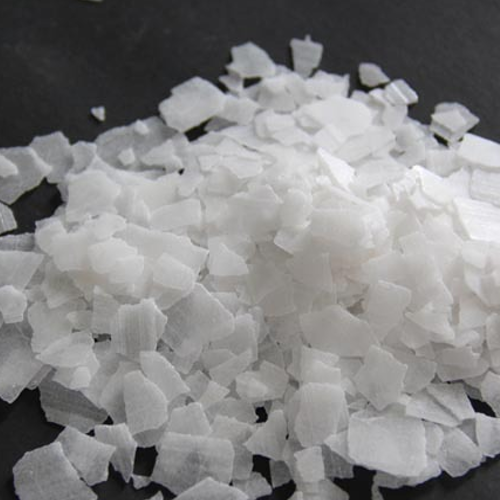

Caustic Soda Flake (sodium hydroxide flake) are prepared by liquid caustic soda which is produced by membrane cell technology. Therefore, this product has the best quality and is without heavy metal impurities. Caustic soda flake are highly hygroscopic and soluble in water and are used in a lot of different industries .The purity of this product is min %99.
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound. It is a white solid and highly caustic metallic base and alkali salt which is available in pellets, flakes, granules, and as prepared solutions at a number of different concentrations. Sodium hydroxide forms an approximately 50% (by weight) saturated solution with water. Sodium hydroxide is soluble in water, ethanol and methanol. This alkali is deliquescent and readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide in air.
Caustic soda flake is produced from soda lye in from liquid form (membrane electrolysis) at the flaking plant built on the license of the Swiss company Bertram’s. Caustic soda is an inorganic chemical compound belonging to the group of the strongest alkalis; Caustic soda is highly hygroscopic and soluble in water and alcohols. Caustic soda flake is one of the main raw materials in the chemical industry. Sodium hydroxide is used in most of industries, for example: cosmetics, petrochemical, metallurgical, textile, food or in water treatment. High quality of our product as well as efficient and flexible logistic service allows us to become a preferred supplier throughout Europe and also at overseas markets such as Asia, Africa and South America.
Lye flake (technical sodium hydroxide flakes) – flake mass of white color, very hygroscopic, very soluble in water and alcohol. The formula is NaOH. Technical sodium hydroxide flakes are obtained by evaporating of liquid caustic soda А grade.
Caustic Soda Flake Applications
Caustic Soda Flake is used in organic synthesis processes, petroleum products refining, textile industry in production of viscose silk and in bleaching fabrics, in paper and aniline industry, soap making, production of aluminum and sodium metal, soluble glass, alkaline accumulators, Trilon B.
Caustic soda flakes are transported by railway and motor transport. 25 kg, 50 kg polypropylene bags, special soft containers with a maximum mass of 1,000 kg, 60 kg polyethylene barrels (without the insert) are used for packaging the product. Transportation in 20 and 40-feet sea vans is possible for countries outside the CIS.
Caustic Soda, Lye is one of the most widely used chemicals in the industry. Caustic soda is a commitment, we guarantee a high service level towards our customers.
Worldwide, the major users of caustic soda are the aluminum industry, pulp & paper and the chemical industry. The main applications are water treatment and water purification, as cleaning agent, or a wide range of uses in chemical industry like starch production or for the desulphurization in the petrochemical industry.
solution of Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in water. Caustic soda is a strong base with a wide range of applications in different industries. We produce caustic soda together with chlorine and hydrogen from the electrolysis of salt brine. With our production in five plants in Europe and our quality
LYE Flake Packing
We have two kind of packing for caustic soda flake, First Lye flake packing is 25kg PP/PE bags in Jumbo Bag (per jumbo bag is weight is .250MT). The next packing form is: 25kg PP/PE shrinking on pallet.
LYE Uses
Caustic soda flake , or sodium hydroxide, mostly used by industry and chemical manufacturing companies. Some

fields caustic soda use for :
– Refineries Alumina
– plastic wrap
– Soaps and cleaners
– Detergent
– Textile processing
– Oil refining
– Water treatment
– Metal processing
we are exporting flake Lye to many destinations all over the world, such as Middle east, African and Europe countries, by the best quality and the most competitive price.
Caustic Soda Flake Formula
Flake Lye is knowing by some name and formula according to application in different industries, such as:
Sodium hydroxide ( NaOH), purity / mass: Min. 99.50
Chlorides / NaCl, purity / mass: Max. 0.10
Sodium carbonate / Na2CO3, purity / mass, Max. 0.40

Sulphur
Sulphur Description

Sulphur (Sulfur) is one of the most important agricultural and industrial raw materials and is considered a strategic product sulfur is an odourless, tasteless and polyvalent nonmetal which is mostly in the form of yellow crystals and is obtained from sulphide and sulphate. Sulphur occurs naturally in the environment and is the thirteenth most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It can be mined in its elemental form, although this method has declined over the last decade to less than 2% of world production. Today most elemental sulphur is obtained as a co-product recovered from oil and gas production in sweetening process.
The Greeks called it “theion”, the Romans “Sulfur” and the Anglo-Saxons “brimstone” – regardless of its name one thing is certain, Sulfur is vital for life.
Sulfur (also spelled Sulphur) is a chemical element with symbol S and atomic number 16.
We, as one of the main key players in supply and export of granular and lumps sulfur from Iran and Turkmenistan, are in position to supply and export sulfur for your esteemed company with competitive prices, flexible payment terms, and required packaging. Therefore, we invite all the traders, distributors and end-users to try us with our quality services and competitive prices.
Sulphur is the primary source in the production of sulphuric acid, the world’s most widely used chemical. Sulphuric acid is an essential intermediate in many processes in the chemical and manufacturing industries. Sulphuric acid also is used by the fertilizer industry to manufacture primarily phosphates, nitrogen, potassium, and sulphate fertilizers.
Sulfur reacts directly with methane to give carbon disulfide, used to manufacture cellophane and rayon. One of the direct uses of sulfur is in vulcanization of rubber, where polysulfide chains crosslink organic polymers. Large quantities of sulfites are used to bleach paper and to preserve dried fruit. Many surfactants and detergents (e.g. sodium lauryl sulfate) are sulfate derivatives. Calcium sulfate, gypsum, is mined on the scale of 100 million tonnes each year for use in Portland cement and fertilizers. Sulphur is increasingly used as a component of fertilizers. Sulfur can be used in agriculture and various industries such as plastics and many synthetic products, paper, paint, etc.
The increasing demand from the fertilizer manufacturing sector, coupled with increasing usage of sulfur for vulcanization of rubber are the main factors driving the growth of the global sulfur industry. Moreover, owing to the fall of crude prices, refineries across the globe are engaging in capacity expansion and other brownfield activities, leading to higher demand for sulfur. The demand for sulfur is also anticipated to be driven by the increasing usage of elemental sulfur as a major ingredient in the vulcanization process implemented to manufacture rubber. However, the enactment of stringent environmental regulations restricting the usage of sulfur and the high costs associated with its mining, are the key factors hindering the sulfur market growth.
The global market is segmented based on end-user applications, including agrochemicals, chemical processing, metal manufacturing, petroleum refining, and others. In 2016, the agrochemical industry occupied the largest share in terms of sulfur consumption. It is expected that the healthy growth of the phosphate fertilizer market will drive the global sulfur market over the forecast year.
Geographically, the market has been segmented into North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Middle East & Africa. Asia-Pacific represents the largest market in terms of consumption and production of sulfur. In the region, China is expected to be one of the largest producers of sulfur and sulfuric acid. Currently, the country imports more than a third of the global sulfur` trade. This group is able to provide sulfur with the highest quality in two kinds of granule and lump.
Sulphur Uses
– Sulfur is Used in Fireworks and Black Gunpowder
– as a fungicide , fumigant , and in the vulcanization of rubber
– in the manufacture of phosphate fertilizers
– in the treatment of certain akin diseases
– the most important compound is sulfuric acid
– Other important compounds include Sulfur dioxide , used as a bleaching agent , disinfectant and refrigerant
Sulfur Application
Agricultural fertilizer use: sulfur is an essential plant nutrient needed for the production of amino acids which in turn make up proteins.
Pure elemental sulfur is a vital secondary macronutrient that can be applied to deficient soils or in places where it is necessary to lower pH for acid loving plants. It is granulated for easy application through any type spreader.
Sulfur is essential in the structural and enzymatic components in plants. Sulphur is a key component of some essential amino acids and is needed for protein synthesis. Chlorophyll synthesis also requires S.
Sulfur (Sulphur) is not readily translocated within plants, so all plants need a continuous supply of Sulphur from emergence to crop maturity. Therefore, in S-deficient plants, older leaves may appear more healthy, while newer leaves and tissue may have stunted growth and a lighter green or even yellow appearance.
Most compound fertilizers containing Sulphur also contain nitrogen, highlighting the close link between these two elements. Sulphur is part of an enzyme needed for nitrogen uptake and lack of it can severely hamper nitrogen metabolism. Together with nitrogen, sulphur enables the formations of amino acids required for protein synthesis. It is found in fatty acids and vitamins and has an important impact on quality and taste or smell of crops.
Non-agricultural uses:
It is widely used in many consumer products and industrial applications. It’s commonly converted to sulfate prior to use in rubber, textile, detergent and paper.
Sulfur Packing
Our Sulfur Mineral 20-30%, is offered in three different shapes, Lumps, Grinded and powder. Sulphur packing will be in Bulk, 25 KG PP bags or Jumbo Bags.
Urea
Urea Description

Urea (carbamide), readily produced from ammonia and carbon dioxide, is a very important chemical in the agricultural and the polymer industries.
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic. Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. introduction and scientific invention of Urea is identified as a life changing event in the history of agriculture. Urea N46% is the world’s most common nitrogen fertilizer and has been used uniformly in all the agricultural lands of the world. Never before this, agriculture had seen such booming heights in production as well as prosperity. Urea is neutral in pH and can adapt to almost all kinds of soils. It is a waste product formed naturally by metabolizing protein in humans as well as other mammals, amphibians and some fish. Urea is widely used in the agricultural sector both as a fertilizer and animal feed additive.
The last decade has seen urea (carbamide) as a superb replacement to ammonium nitrate and has unleashed new unsurpassed production records. The white, crystalline solid comprises of a proportionate compound mixture of more than one nutrients and contains 46% nitrogen. Farmers have identified with this chemical fertilizer as a great ladder to huge success in agro revolution. The nutrient composition rendered by urea enhances the productivity of the soil and enriches its nutrient constituency. Providing each plant with relevant elements needed, urea sustains plant life.
More than 90% of world industrial production of urea is destined for use as a nitrogen-release fertilizer. Urea has the highest nitrogen content of all solid nitrogenous fertilizers in common use. Therefore, it has the lowest transportation costs per unit of nitrogen nutrient. Urea fertilizers rapidly transform to the ammonium form in soils.
Worldwide, urea N46% is one of the most widely used dry granular sources of nitrogen. It is preferred by the fertilizer manufacturing industry since it is relatively easy to manufacture. Urea also has a high nitrogen content (46%), in comparison to other popular nitrogen sources (i.e. ammonium nitrate). On a ton for ton basis, urea contains 35% more nitrogen than ammonium nitrate. This has implications on the storage and transport of nitrogen fertilizer products. Carbamide is considered a relatively stable product to store and transport, and it is for this reason that the transportation of Carbamide is considered very cost effective in comparison to its most common alternative, ammonium nitrate.
Advantages of Carbamide Fertilizer
– Superior Nitrogen content
– Low production cost, as source is natural
– Non-flammable and risk-free storage
– Wide application range, for all types of crops and soils
– Neutral pH and harmless to crops and soil
In 2022, the potential supply of urea fertilizers is expected to reach 197 million metric tons. Increasing crop prices lead to increased fertilizer demands and has been especially noted in recent years in South Asia. Favorable weather also increases demand for fertilizers in major agricultural regions.
Urea Uses
Urea is the world’s most commonly used nitrogen fertilizer and indeed more of it is manufactured by mass than any other organic chemical. Containing 46% N, it is the most concentrated nitrogen fertilizer, and is readily available as free-flowing prills (granules). It is the cheapest form of nitrogen fertilizer to transport and it is also the least likely to ‘cake’. It is therefore favoured in developing countries.
While over 90% of urea produced is used as a fertilizer, it has other uses, which include the manufacture of the melamine, used in melamine-methanal resins. Urea itself also forms important resins.
An increasingly important use of Carbamide is in reducing air pollution from diesel engines in cars, buses and lorries. Diesel engines run at high temperatures and nitrogen and oxygen, from the air, are able to react together under these conditions to produce high concentrations of nitric oxide. One way to remove this pollutant is to allow it to react with ammonia to form nitrogen.
However it is not possible to use ammonia directly as it is too volatile and is poisonous. Instead a solution of urea in water is injected into the hot gases emerging from the engine in the exhaust. It is thermally decomposed to ammonia and carbon dioxide. This is the reverse of the process used to make ammonia:
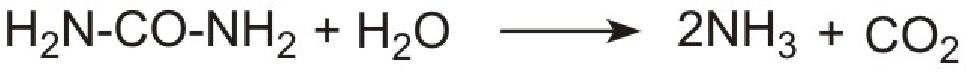
Unlike ammonia, urea is safe and easy to handle. The products, ammonia and carbon dioxide, together with the exhaust gases, are passed immediately over a catalyst in the exhaust system. Ammonia reduces the oxides of nitrogen (mainly nitric oxide), formed in the combustion processes, to nitrogen. The process is complex but the overall reaction can be represented thus:
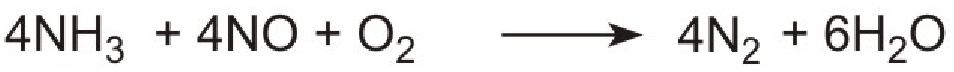
The system is known as Urea SCR (urea-based selective catalytic reduction) and can reduce pollution by nitrogen oxides to almost zero.
Annual Production of Carbamide
| World | 164 million tons |
| China | 62 million tons |
| India | 23 million tons |
| Middle East | 20 million tons |
| Rest of Asia | 18 million tons |
| FSU | 12 million tons |
| North America | 9.5 million tons |
| Europe | 9.5 million tons |
Urea Specifications
| Typical Chemical Analysis |
| Parameter Specification |
| Total Nitrogen Content, % 46.0 |
| Moisture content, wt. % 0.1 – 0.4 |
| Biuret, wt. % 0.85 – 1.5 |
| Conditioning agent, wt. % 0.30 – 0.60 |
| Typical Physical Properties |
| Parameter Specification |
| Bulk density, lb/ft3 48 – 52 |
| Angle of repose 28 – 32o |
| Size Guide Number (SGN) see note 1 240 – 320 |
| Uniformity Index (UI) see note 1 50 – 55 |
Packing of Carbamide N46
Packing in 50 kg polypropylene bags accepted up to 2000mt, for more quantities Bulk is available.
Linear Alkyl Benzene Sulphonic Acid
Sulfonic Acid (LABSA) Description

Sulfonic Acid (LABSA) is a batch of organic Sulfur compounds that are used as an anionic surfactant in most home detergents such as dishwashing detergents and washing powders. LABSA compound is used as a cleaning agent, foaming agent and sponge cleaner in more formulations. For the production of Sulfonic Acid, alkaline benzene linear sulfation is usually used. And its ingredients Linear Alkylbenzene, Oxygen, Sulfur and Citric Acid.
Linear Alkyl Benzene Sulphonic Acid is an anionic surfactant with molecules characterized by a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic group. They are non-volatile compounds produced by sulfonation. Linear alkylbenzene sulfonic acid are complex mixtures of homologues of different alkyl chain lengths (C10 to C13 or C14) and phenyl positional isomers of 2 to 5-phenyl in proportions dictated by the starting materials and reaction conditions, each containing an aromatic ring sulfonated at the para position and attached to a linear alkyl chain at any position with the exception of terminal one (1-phenyl).
The starting material LAB (linear alkyl benzene) is produced by the alkylation of benzene with n-paraffins
in the presence of hydrogen fluoride (HF) or aluminum chloride (AlCl3) as a catalyst, the latest is DETAL
process by UOP. LABSA is produced by the sulfonation of LAB with sulphuric acid in batch reactors.
Other sulfonation alternative reagents are oleum, diluted sulfur trioxide, chlorosulfonic acid and sulfamic
acid on falling film reactors.
Uses of Sulfonic Acid (LABSA)
High action of detergency, moistening, foaming, emulsion. Widely applied in a variety of detergents and emulsifiers, such as washing powder, daily-use chemical detergent, utensils detergents and textile industry of the cleaning agent, dye, electro plating industry, leather industry, degreasing agents and paper industry’s de-coloring agent. Household detergents including laundry powders, laundry liquids, dishwashing liquids and other household cleaners.
-It is used in anionic specialty formulations.
-In other industries such as textile industries, it is used as an mercerising or washing agent.
-It is used to increase the surface area of distempers.
-As main active matter in all forms of Detergents like Cake, Powder and Liquid formulations.
-As emulsifier and wetting agent in small quantity with other surfactants in Toilet soaps for foaming.
-In Pesticides to improve the quality of spray.
Sulfonic Acid (LABSA) Characteristics
- Chemical Formula : R-C6H4-SO3H
- CAS Number: 27176-87-0
- Active Matter (M=320) 96.0 % – 98.0%
- Specific Gravity (20°C) 1.050 – 1.060
- Free Oil < 2.5%
- Sulfuric Acid < 0.75%
- Preservation none
- Neutralization Index 13 (g NaOH 100/100 g)
- Color, APHA; ASTM D 1209 (Klett 5% AM) < 80
- Water Content 0.55%
LABSA Specifications
| Active ingredients | 97% (Min.) |
| Free Sulphuric Acid | 4-7% (Max) |
| Free Oil | 1% (Max) |
| Color Klett | 35 When packed (Max) |
| Density (gm/ml at 200c) | 1.07 |
| Appearance | Light Yellow-Brown Liquid |
| Viscosity | Low Viscosity |
| Mean Molecular Mass | Average 326 |
LABSA Packing

Sulfonic Acid or LABSA can be packed in 200 Kg PE Drums or 1 MT IBC Tanks.
80 Drums can be palletized and loaded in 1 full 20ft container.
20 IBC Tanks can be loaded in 1 full 20ft container.
Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR)
Butadiene Rubber

Polybutadiene rubber is rubber for general use. The most usage of butadiene rubber is tire sidewall, floor covering-bicycle tire, foot wear, rubber toy, cable and rubber pipes. They are produced by butadiene. It may be present in macromolecules in form of cis-1.4, trans-1.4 and 1.2 structural units. 1.2 units have pendant vinyl group; thus, they may create isomeric forms (syndiotactic, isotactic or atactic).
Content of individual forms of butadiene rubber structural units in polymeric chain depends on the polymerization method and type of used initiator and it determines basic properties of butadiene rubber.
Butadiene rubber-BR is a synthetic rubber. Polybutadiene rubber is a polymer formed from the polymerization of the monomer 1,3-butadiene. Polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tires, which consumes about 70% of the production. Another 25% is used as an additive to improve the toughness (impact resistance) of plastics such as polystyrene and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). Polybutadiene rubber accounted for about a quarter of total global consumption of synthetic rubbers in 2012.
Butadiene rubber, synthetic rubber widely employed in tire treads for trucks and automobiles. It consists of polybutadiene, an elastomer (elastic polymer) built up by chemically linking multiple molecules of butadiene to form giant molecules, or polymers. The polymer is noted for its high resistance to abrasion, low heat buildup, and resistance to cracking.
Description of Poly Butadiene Rubber (PBR)
Polybutadiene [butadiene rubber BR] is a synthetic rubber. PBR is a polymer formed from the polymerization of the monomer 1, 3-butadiene. Polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tires, which consumes about 70% of the production. Another 25% is used as an additive to improve the toughness (impact resistance) of plastics such as polystyrene and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). PBR accounted for about a quarter of total global consumption of synthetic rubbers in 2012. It is also used to manufacture golf balls, various elastic objects and to coat or encapsulate electronic assemblies, offering high electrical resistivity.
Application of Poly Butadiene Rubber
ATDM 1220 is appropriate for rubber compounds used in:
- the inner tube of hoses for sandblasting, along with natural rubber.
- cover of hoses, mainly pneumatic and water hoses.
- railway pads, bridge blocks, etc.
- manufacturing of the high-restitution toy Super Ball.
- fuel in combination with an oxidizer in various Solid Rocket Boosters such as Japan’s H-IIB launch vehicle.
- Tires
- Conveyor belts
- Crack pads
- Footwear soles
- V-belts
- Golf balls
Packing of Polybutadiene Rubber
35 ±0.5 KG bales wrapped with polyethylene film.
36 bales per crate (1260±18 KG).
Specification of Polybutadiene Rubber
| Typical Properties | Units | Values | Test methods |
| Compound Mooney Viscosity | MU | MAX 77 | ASTM D – 1646 |
| Tensile Strength(35 Min) | Kgf/cm3 | MIN 150 | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break (35 Min) | % | MIN 440 | ASTM D412 |
| 300% Modulus at 145 °C | |||
| 25 Min | Kgf/cm3 | 68-108 | ASTM D412 |
| 35 Min | Kgf/cm3 | 74-114 | ASTM D412 |
| 50 Min | Kgf/cm3 | 74-114 | ASTM D412 |
Asphalt oil
Asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term asphaltum was also used. The word is derived from the Ancient Greek ἄσφαλτος ásphaltos. The Pitch Lake is the largest natural deposit of asphalt in the world, estimated to contain 10 million tons.
Petroleum Asphalt
Petroleum asphalt is a sticky, black and highly viscous liquid or semi-solid that is present in most petroleum crude oils and in some natural deposits. Petroleum crude oil is a complex mixture of a great many different hydrocarbons. Petroleum asphalt is defined as that part of crude oil which is separated from the higher-boiling hydrocarbons in crude oil by precipitation upon the addition of lower-boiling hydrocarbon solvents such as propane, pentane, hexane or heptane. The precipitated material consists of asphaltenes which have an average molecular weight of about (800 – 2500 g/mole) and exist in the form of flat sheets of polyaromatic condensed rings with short aliphatic chains.
Over the years, petroleum asphalt has been referred to as bitumen, asphaltum or pitch. The terminology varies from country to country and from individual to individual. Asphalt is often confused with coal tar (or coal pitch) derived from the pyrolysis of coal and which has a different chemical structure than asphalt.
When petroleum asphalt is combined with construction aggregate (sand, gravel, crushed stone, etc.) for use in road construction or paving, it has often been referred to as asphaltic concrete, asphaltic cement, bituminous concrete, blacktop or road tar.
Asphalt Oil

Technology of asphalt pavements by asphalt oil started 170 years ago, with an experiment involving natural rubber with bitumen in the 1840s, attempting to capture the flexible nature of rubber in a longer lasting paving surface. Now a day’s especially rubber process oil use instead of natural rubber for bitumen rubber blend as asphalt oil for pavement.
Nowadays the rubberized asphalt technology is being adopted in many other parts of the world: Taiwan is pioneer inasphalt mixtures for flexible pavement rehabilitation; furthermore, rubberised asphalt oil has been trialled in Beijing and for use in new and maintenance work as part of the preparation for the 2008 Olympics in China and it has also been used in EcoPark Project in Hong Kong.
Blending rubber oil with bitumen in asphalt
The principal objects of adding rubber to bitumen are to give the bitumen elasticity, to increase its ductility and to reduce its susceptibility to temperature changes. The effectiveness of rubber in bringing about these desirable changes depends on the extent to which the rubber dissolves in the bitumen. To dissolve read ily, the rubber must be unvulcanised and be in a finely divided state. Rubber exists in this condition in the form of latex, and it is known to add rubber in this form both to bitumen emulsions and to hot bitumen and to add rubber in the forms of vulcanized and unvulcanised rubber powder to hot bitumen and to asphalt paving mixtures during the process of mixing.
Distillate Aromatic Extract (DAE)
Description of Distillate Aromatic Extract

Distillate Aromatic Extract is an aromatic oils with a large number of aromatic cycles in their composition; they are characterized by their low aniline point and their high solvent power. They are primarily used in formulation with polar rubbers of the SBR and NR types.
DAE aromatic rubber oil (distillate aromatic extract, abbreviated as DAE) distillate aromatic extracts have very high aromatic contents. DAEs are obtained as a byproduct of the process of solvent extraction of vacuum distillates used as a raw material in the manufacture of p m lubricant base oils. DAE grades are DAE 10 , DAE 11 , DAE 20 , DAE 40 ,DAE 50 , DAE 60 .
Estimation of mixture behaviors was accomplished through the use of a suite of representative structures that are expected to be present in these DAEs. In general, the components of DAEs are poorly soluble in water, very hydrophobic, and moderately to poorly volatile, although some will evaporate readily from water. DAEs are expected to predominantly reside in sediment and soil, with some lighter components partitioning to air.
Application of Distillate Aromatic Extract
DAE distillated aromatic extract combination is used as:
- Carrier oils
- Plasticizer
- Diluents & filling agent
- Good Solubility Properties
- processing ability of rubber in milling and mixing
- Heavy fuels
- Feed stock for production of carbon black
- Petroleum pitches and resins
- Manufacture of rubber and plastics
Packing of Distillate Aromatic Extract
Packing DAE10, DAE20, DAE40, DAE50, DAE60 can be in new steel drum, one new steel drum capacity is 200-210 liter , recondition or used drum also can contain same quantity per drum totally 16.500 to 17.000 MT DAE different grade can load on one 20foot container equal to 80 drum , ISO tank capacity is 20 MT net weight same as flexi tanks.
Specification of DAE
| Characteristic | Test method | 60 | 50 | 40 | 20 | 11 | 10 |
| Kinematic viscosity @ 100°C, cSt | ASTM D-445 | 60.0 | 50.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 11.0 | 10.0 |
| Flash point, °C | ASTM D-92 | 300 | 265 | 265 | 240 | 215 | 215 |
| Pour point , °C | ASTM D-97 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 15 | 9 | 9 |
| Specific gravity @ 15 , Kg/m3 | ASTM D-1298 | 995 | 1020 | 1010 | 1005 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Aniline point, °C | IP-2 | 65 | 40 | 50 | 45 | 30 | 35 |
| Sulphur content, Wt% | ASTM D-2622 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| Ash content , Wt% | ASTM D-482 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Carbon type analysis , % | |||||||
| CA | ASTM D-3238 | 35 | 50 | 30 | 40 | 60 | 55 |
| CN | 5 | 5 | 4 | 15 | 1 | 1 | |
| CP | 60 | 45 | 65 | 45 | 39 | 44 |
Treated Distillate Aromatic Extracts (TDAE)
Description of Treated Distillate Aromatic Extracts

Treated distillate aromatic extracts (TDAE) is a rubber processing oil with high aromatic content. It is used rubber softening additive in the process of vulcanization of rubber. Its high viscosity-gravity constant has made it highly preferable in the tire manufacturing applications, thereby, reducing heat buildup. Due to this characteristic of treated distillate aromatic extracts, it is possible to produce large rubber based intermediate products.
TDAE (Treated Distillate Aromatic Extract.) is a non-carcinogenic mineral oil, used as aromatic process oils for the manufacture of oil extended natural or synthetic rubber and tire compounds. This environment friendly process oil is used as a softening additive in the process of vulcanization of natural rubber and as a component of rubber compounds. Its high viscosity gravity constant (VGC) leads to the reduction in heat buildup and rotational resistance during the usage of tires. Such characteristics enable our TDAE to be used in the production of high quality tire and rubbers.
TDAE is Eco friendly rubber oil which is according European standard , low PCA content which is below 3% makes TDAE as safe oil , more than 3% of PCA may cuase skin cancer in human, also PAH should be below 10 ppm .
The global TDAE market has been experiencing moderate growth in terms of consumption over the past few years. The market is heading towards growth expansion and it is expected to grow progressively in the coming years. Demand for TDAE is largely belongs to the growth of the transportation industry. It is primarily used in the production of the tire, which is highly required in the transportation industry. As per the industry experts, transportation industry is poised to grow beyond USD 1.3 trillion by 2020, expanding at dynamic CAGR of over 8%, and likely to set enhanced consumption of TDAE. Rubber products are being increasingly used in a broad spectrum of application in the industries ranging from the agriculture to textile with emergence of FMCG sector as a game changer. Widening application scope of TDAE is providing enhanced growth prospects year by year to this market. On the split side, TDAE contains high polymeric hydrocarbon content which us highly hazardous to the environment. Due to which European Union have regulated strict regulation on the consumption of TDAE and regulations are further followed by non-European countries by restraining the global demand for TDAE.
Treated distillate aromatic extract (TDAE), used as rubber softening additive in rubber processing, and rubber has diverse application across the industrial manufacturing. Increasing industrial output as a result of rising industrial manufacturing is set to uplift the consumption of TDAE and is likely to provide tremendous growth opportunities.
Application of Treated Distillate Aromatic Extracts
- industry ink formulations
- isolation manufacturers
- automobile tire making factory
- rubber manufacturing
- shoes
- flooring
- cables and any other industrial interface
- as an ingredient (softener/plasticizer)
- as a processing aid in the production of natural and synthetic rubber products.
- as an ingredient in certain engine, gear and lubricating oils.
Packing of TDAE
Packing can be in new steel drum, recondition or used drum also can load on one 20foot container equal to 80 drum , ISO tank capacity is 20 MT net weight same as flexi tanks.
Specification of TDAE:
| Characteristic | Unit | Result | Test Method |
| Sp.gr @ 15˚C | kg/m3 | 953 | ASTM D-1298 |
| Flash Point | ˚C | 246 | ASTM D-92 |
| Congealing Point | ˚C | 33 | ASTM D- 938 |
| TAN | mg KOH/gr | 0.12 | ASTM D-974 |
| Kinematic Viscosity@40°C | cSt | 549.48 | ASTM D-445 |
| Kinematic Viscosity @50 °C | cSt | 260.8 | ASTM D-445 |
| Kinematic Viscosity @100 °C | cSt | 19.65 | ASTM D-445 |
| RI@20˚C | — | 1.5227 | ASTM D-1218 |
| RI@67˚C | — | 1.5113 | ASTM D-1218 |
| VGC | — | 0.895 | ASTM D-2501 |
| Aniline point | ˚C | 63 | ASTM D-611 |
| Refractivity Intercept | — | 1.051 | AMS140.13 |
| Water Content (Karl Fischer) | ppm | 412.2 | ASTM D-6304 |
| Sulphur Content | %(W/W) | 3 Max | ASTM D-2622 |
| Carbon Type Distribution | % CA/CN/CP | 23/39/38 | AMS 140.13 |
| Content Of PCA Extract | %(W/W) | 2.2 | IP 346 |
Paraffinic Rubber Process Oil
Description of Paraffinic oils
This category of hydrocarbons constitutes branched chain or straight linked hydrocarbon molecules of various viscosities. Because the chain length will increase, the viscosity will increase, and also the rubber process oil becomes a lot of viscous. They find extensive usage in ethylene-propylene rubbers.
These are more stable and have the highest flash purpose for a given viscosity. This class of hydrocarbons constitutes branched chain or straight linked hydrocarbon molecules of various viscosities. As the chain length increases, the viscosity increases and the RPO becomes more viscous.
They find extensive usage in EPDM, Butyl rubbers. Include Paraffinic oils with high viscosity and high flash point is good for shelf life of the end product. The high viscosity and high flash point paraffinic oils are extensively used in EPDM profiles for automotive applications.
Advantages of Paraffinic oils
Paraffinic Oils are generally light in color having wide viscosity range, higher Aniline &Flash Point. It is extensively used in the manufacturing of butyl tubes, EPDM based rubber products, such as profiles, hose pipe& automotive Components.
Aromatic Rubber Process Oil
Description of Aromatic oils
The primary Characteristics of aromatic Hydrocarbons are the presence of the double bonded mix ring carbon structure. Aromatic extender oil well-known according to its viscosity which meets ASTM D-445 and Kinematic viscosity of transparent and opaque liquids it has different grades famous as high(heavy), medium, low (light) viscosity, TDAE, MES, and DAE.
Aromatic furfural extract rubber process oil (RPO) procured from selected refineries and suitably blended to meet stringent specifications, are used for compounding batches to manufacture tires, lactic, automotive tires and tubes, bicycle tires, tire re-treading materials, belting, hoses, battery casings and containers, extruded products, technical molded goods and rubber articles with reclaim rubber due to high solvency, calendared and molded sheets, Tread rubber TDAE oil. Also process oil (furfural extract) has color stability, solubility, and good thermal stability.
Aromatic Rubber Process Oil (RPO) is rich aromatic by products from solvent extracting process to modify physical properties of the vulcanization and to reduce the cost of the finished product.
Iran rubber process oil is special furfural extract RPO which can be broadly classified into two different groups (as below) depending on the physical arrangement of the carbon atoms. Paraffinic, aromatics. Rubber Process Oil are used during mixing of rubber compounds. These help in improving the dispersion of fillers and flow characteristics of the compound during further processing. Rubber process oil are specially developed taking into consideration the type of rubber and the end product applications.
Application of Aromatic RPO
- Used in manufacturing of products such as tires for automobiles, trucks and construction machinery, manufacture of microwave
- Used in connectors for household appliances such as washing machines and dishwashers, rubber roller
