Cationic Bitumen Emulsion CSS-1h
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion CSS-1h Definition

Cationic Bitumen Emulsion CSS-1h is a cationic emulsion. Bitumen emulsions CSS-1h are usually made by passing the mixture of hot bitumen and water phase between a rotating disc, cone, or wheel and a stator. In the emulsification process, the hot binder is mechanically separated into minute globules and dispersed in water treated with a small quantity of the emulsifying agent. The water is called the continuous phase and the globules of the binder are called the discontinuous phase. by proper selection of an emulsifying agent and other manufacturing controls.
Bitumen emulsion consists of three basic ingredients: bitumen, water, and an emulsifying agent. Based on specifications it may contain other additives, such as stabilizers, coating improvers, anti-strips, or break control agents. It is well known that water and asphalt will not mix, except under carefully controlled conditions using highly specialized equipment and chemical additives.
Cationic bitumen emulsions CSS-1h have a positive charge and hence a direct and very rapid reaction between the emulsion and aggregate or pavement is possible. The size of the charge or the Zeta potential affects stability, the larger the charge the greater the repulsion, but as the aggregate is negatively charged the higher the zeta potential the more rapid the reaction.
So it is possible to stabilize a cationic emulsion in the same way that makes it a more rapid break. The other mechanism of evaporation is available too but as the emulsion is stabilized this form of break becomes slower. Thus a balance must be struck. After the electrostatic part of the reaction is complete the emulsion will rely on flocculation and coalescence to complete break.
After the break is completed the water must still be completely evaporated for the residual Asphalt to achieve full strength.
Bitumen Emulsion CSS-1h ASTM is designed for use in slurry seals and for cold storable mixtures for patching. They are designed for soil stabilization and also suitable for use with cold recycling. These emulsions are tailor-made as per the quality of aggregates and local site conditions.
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion CSS-1h Applications
Cationic emulsions may be used at ambient temperatures with aggregates, which need not be completely dry. Emulsions are less hazardous to use in comparison with cutback and can be applied in a wider range of conditions. Most CSS-1h applications are listed below:
- Biturubber (Rubber)
- Bitumalch (Malching)
- Prepared cold Mixed Asphalt
- Bituprime (Prime Coat)
- Bitucoat (Fog Seal – Seal Coat)
Successful performance of bitumen emulsions requires selecting the proper type and grade for the intended use. Guidelines presented in this chapter should help select the specific grade and type of emulsion to be used.
The first consideration in picking the right type and grade of the emulsion is how the emulsion will be used. Is it for a planned mix (central or mixed-in-place), a recycled mix, or a prime coat application? Is it for some type of surface application, such as a fog seal, slurry seal, micro-surfacing, or chip seal? Is it for a maintenance mix? Once this decision is made, other project variables must then be considered. Some other factors that affect the selection are:
• Climatic conditions anticipated during construction. The choice of emulsion grade, the design of mix or treatment, and the selection of construction equipment should be dictated by the conditions at the time of construction.
• Aggregate type, gradation, and availability.
• Contractor or construction equipment availability.
• Geographical location. The hauling distance and, in some cases, water availability are important considerations.
• Traffic control. Can traffic be detoured or only controlled through the work area?
• Environmental considerations.
• Proper application for pavement preservation or pavement distresses.
• Traffic type and volume.
While general guidelines can be given for selecting emulsions, laboratory testing is strongly recommended. There is no substitute for laboratory evaluation of the emulsion and the aggregate to be used. Different types and quantities of an emulsion should be tried with the aggregate to find the best combination for the intended use. An experienced technician can determine the type and grade of the emulsion to be used.
Cationic emulsions are preferred for use with negatively charged siliceous aggregates such as quartz, granite, sandstone, and river gravel. In general, Cationic emulsions can be used with a wider range of aggregates, will tolerate greater quantities of moisture, and will break at a lower ambient temperature. The main application areas of Emulsion bitumen are surface dressing, tack coats, prime coat, slurry seal, and cold mixing.
Dust control (SS-1, CS-1, CRS-1)
Tack coat (SS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1, CSS-1h, CRS-1)
Prime coat (SS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1, CSS-1h)
Fog seal (SS-1, CSS-1, MS-1-CMS-2, CRS-1)
Penetration prime (SS-1)
Cold mix asphalt, Mulching, Asphalt Sealers (CSS-1)
Chip seal, single, or multiple treatments (RS-1, RS-2, HFMS-1, HFMS-2, HFRS-2, CRS-2, and CRS-2P)
Sand seal (SS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1, CSS-1h, CMS-2s, CRS-1, CRS-2)
Slurry seal (SS-1h, CSS-1h, CSS-1Hp)
Sandwich seal, cape seal, chip seal (CR-2)
Micro surfacing (CQS-1h)
Structural and surface plant mixture (SS-1, SS-1h, HFMS-2s, CSS-1, CSS-1h,)
Stockpiled patching mixture (HFMS-2s, CMS-2s)
In-place road mixing (SS-1, SS-1h, HFMS-2s, HFMS-2, HFMS-2h CMS-2, CMS-2h, CSS-1, CSS-1h)
Crack filler, joint coating (RS-2, HFMS-2h, MS-2, CMS-2h, CRS-2P)
Asphalt sealers, Immediate Maintenance, Stockpile Maintenance Mixes (CMS-2)
Immediate Maintenance (CM2, CM2h)
CSS-1h Advantages
• No petroleum solvent required to liquefy
• Little or no hydrocarbon emissions
•Because of the low viscosity of the Emulsion as compared to hot-applied Bitumen, The Emulsion has good penetration and spreading capacity.
• In most cases, used with no additional heat. It does not need any pre-heating. Thus results in the case of handling for the user, besides saving in cost.
• The ability to coat damp aggregate
• Can use cold materials at remote sites. Cold application of Bitumen Emulsion ensures safety to the workforce; it is a user-friendly product. Being cold-applied the work progresses much faster.
• Wide variety of emulsion types available today
• Economical
• Free from danger ( for fire )
• Environmental
• Harmless for worker health.
• It can use with moisture aggregates. It can be used even with wet aggregates thus enabling users to carry out work during the monsoon also.
• Application temperature is low and does not need heating while storage and transportation period. For this reason, it provides energy saving.
• Emulgators increase adhesion they effect as an anti-stripping agent
• It can use in four seasons. Especially it gives a chance application in the rainy region and it extends the application period.
• It has a lot of application area and construction methods.
• Bitumen Emulsion does not require petroleum solvent to make them liquid as in cut back and also it is not required to be heated like normal Bitumen. Thus saving imported petroleum oil or firewood.
• Toxic fumes (Hydrocarbon emission) normally emitted from heated bitumen & cutbacks not present when Cationic Bitumen Emulsion is used, as no heating is required for its application.
• Energy saving & control of pollution & safety:
During the last 10-12 yrs., the country was in the quest for alternatives to Hot Mixing technology especially to save our beleaguered environment besides curbing the use of Imported petroleum oil, and our precious forests supplying firewood. Optimum use of Bitumen-emulsions can preserve Petroleum Oil and in turn, save our Environment and Foreign Exchange.
CSS-1h Packing
Packing of bitumen emulsion CSS-1h is in a new thick steel drum on a pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Cationic Bitumen emulsion CSS-1h Specification
Emulsion Type: Slow-Setting
Grade: CSS-1h
Standard: ASTM D 2397M – 13
| Properties | Min | Max | Test Method |
| Test on Emulsions | |||
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 25 °C, SFS | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability test, 24-h, % | – | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Particle charge test | positive | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve test, % | – | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Cement mixing test, % | 2.0 | ASTM D6935 | |
| Distillation: | |||
| Residue, % | 57 | – | ASTM D244 |
| Tests on residue from distillation test: | |||
| Penetration, 25°C (77°F), 100 g, 5 s | 40 | 90 | ASTM D5 |
| Ductility, 25°C (77°F), 5 cm/min, cm | 40 | – | ASTM D113 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene, % | 97.5 | – | ASTM D2042 |
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion CSS-1
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion CSS-1 Description
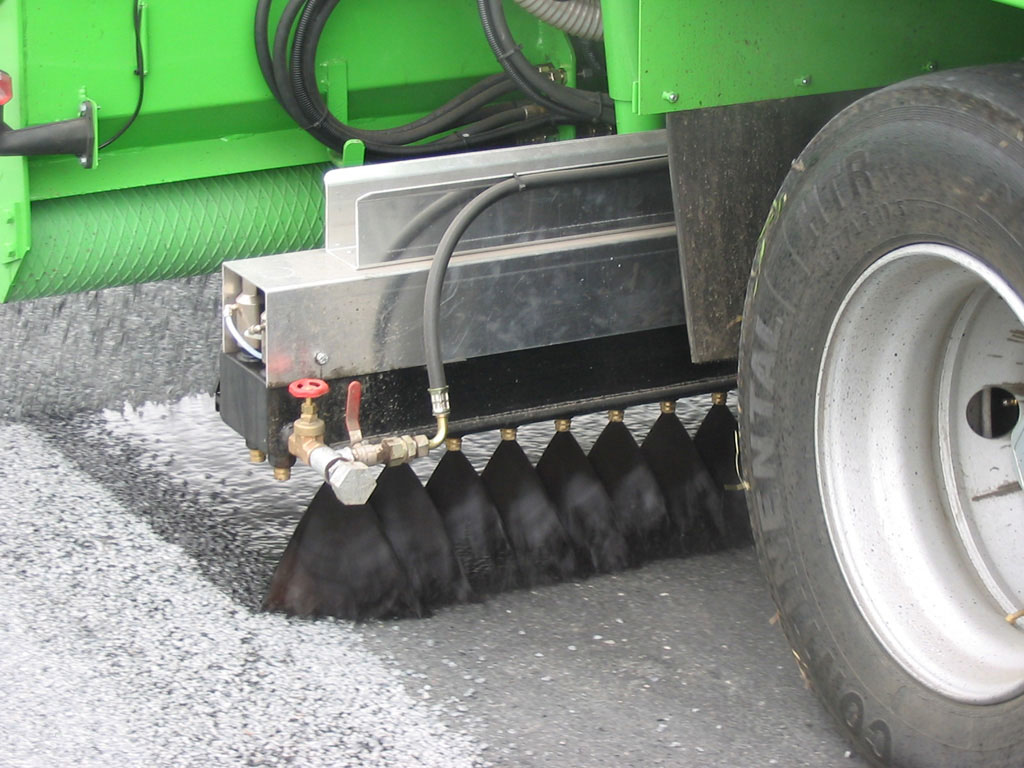

Cationic bitumen emulsions CSS-1 have a positive charge and hence a direct and very rapid reaction between the emulsion and aggregate or pavement is possible. The size of the charge or the Zeta potential affects stability, the larger the charge the greater the repulsion, but as the aggregate is negatively charged the higher the zeta potential the more rapid the reaction.
So it is possible to stabilize a cationic emulsion in the same way that makes it a more rapid break. The other mechanism of evaporation is available too but as the emulsion is stabilized this form of break becomes slower. Thus a balance must be struck. After the electrostatic part of the reaction is complete the emulsion will rely on flocculation and coalescence to complete break.
After the break is completed the water must still be completely evaporated for the residual Asphalt to achieve full strength.
Bitumen emulsion consists of three basic ingredients: bitumen, water, and an emulsifying agent. Based on specifications it may contain other additives, such as stabilizers, coating improvers, anti-strips, or break control agents. It is well known that water and asphalt will not mix, except under carefully controlled conditions using highly specialized equipment and chemical additives.
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion CSS-1 is a cationic emulsion. Bitumen emulsion CSS-1 is usually made by passing the mixture of hot bitumen and water phase between a rotating disc, cone, or wheel and a stator. In the emulsification process, the hot binder is mechanically separated into minute globules and dispersed in water treated with a small quantity of the emulsifying agent. The water is called the continuous phase and the globules of the binder are called the discontinuous phase by proper selection of an emulsifying agent and other manufacturing controls.
Bitumen Emulsion CSS-1 Applications
Cationic emulsions may be used at ambient temperatures with aggregates, which need not be completely dry. Emulsions are less hazardous to use in comparison with the cutback and can be applied in a wider range of conditions. Most CSS-1 applications are listed below:
- Biturubber (Rubber)
- Bitumalch (Malching)
- Prepared cold Mixed Asphalt
- Bituprime (Prime Coat)
- Bitucoat (Fog Seal – Seal Coat)
Successful performance of bitumen emulsions requires selecting the proper type and grade for the intended use. Guidelines presented in this chapter should help select the specific grade and type of emulsion to be used.
The first consideration in picking the right type and grade of the emulsion is how the emulsion will be used. Is it for a planned mix (central or mixed-in-place), a recycled mix, or a prime coat application? Is it for some type of surface application, such as a fog seal, slurry seal, micro-surfacing, or chip seal? Is it for a maintenance mix? Once this decision is made, other project variables must then be considered. Some other factors that affect the selection are:
• Climatic conditions anticipated during construction. The choice of emulsion grade, the design of mix or treatment, and the selection of construction equipment should be dictated by the conditions at the time of construction.
• Aggregate type, gradation, and availability.
• Contractor or construction equipment availability.
• Geographical location. The hauling distance and, in some cases, water availability are important considerations.
the hauling distance and, in some cases, water availability are important considerations.
• Traffic control. Can traffic be detoured or only controlled through the work area?
• Environmental considerations.
• Proper application for pavement preservation or pavement distresses.
• Traffic type and volume.
While general guidelines can be given for selecting emulsions, laboratory testing is strongly recommended. There is no substitute for laboratory evaluation of the emulsion and the aggregate to be used. Different types and quantities of an emulsion should be tried with the aggregate to find the best combination for the intended use. An experienced technician can determine the type and grade of the emulsion to be used.
Cationic emulsions are preferred for use with negatively charged siliceous aggregates such as quartz, granite, sandstone, and river gravel. In general, Cationic emulsions can be used with a wider range of aggregates, will tolerate greater quantities of moisture, and will break at a lower ambient temperature. The main application areas of Emulsion bitumen are surface dressing, tack coats, prime coat, slurry seal, and cold mixing.
Dust control (SS-1, CS-1, CRS-1)
Tack coat (SS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1, CSS-1h, CRS-1)
Prime coat (SS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1, CSS-1h)
Fog seal (SS-1, CSS-1, MS-1-CMS-2, CRS-1)
Penetration prime (SS-1)
Cold mix asphalt, Mulching, Asphalt Sealers (CSS-1)
Chip seal, single, or multiple treatments (RS-1, RS-2, HFMS-1, HFMS-2, HFRS-2, CRS-2, and CRS-2P)
Sand seal (SS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1, CSS-1h, CMS-2s, CRS-1, CRS-2)
Slurry seal (SS-1h, CSS-1h, CSS-1Hp)
Sandwich seal, cape seal, chip seal (CR-2)
Micro surfacing (CQS-1h)
Structural and surface plant mixture (SS-1, SS-1h, HFMS-2s, CSS-1, CSS-1h,)
Stockpiled patching mixture (HFMS-2s, CMS-2s)
In-place road mixing (SS-1, SS-1h, HFMS-2s, HFMS-2, HFMS-2h CMS-2, CMS-2h, CSS-1, CSS-1h)
Crack filler, joint coating (RS-2, HFMS-2h, MS-2, CMS-2h, CRS-2P)
Asphalt sealers, Immediate Maintenance, Stockpile Maintenance Mixes (CMS-2)
Immediate Maintenance (CM2, CM2h)
CSS-1 Advantages
• No petroleum solvent required to liquefy
• Little or no hydrocarbon emissions
•Because of the low viscosity of the Emulsion as compared to hot-applied Bitumen, The Emulsion has good penetration and spreading capacity.
• In most cases, used with no additional heat. It does not need any pre-heating. Thus results in the case of handling for the user, besides saving in cost.
• The ability to coat damp aggregate
• Can use cold materials at remote sites. Cold application of Bitumen Emulsion ensures safety to the workforce; it is a user-friendly product. Being cold-applied the work progresses much faster.
• Wide variety of emulsion types available today
• Economical
• Free from danger ( for fire )
• Environmental
• Harmless for worker health.
• It can use with moisture aggregates. It can be used even with wet aggregates thus enabling users to carry out work during the monsoon also.
• Application temperature is low and does not need heating while storage and transportation period. For this reason, it provides energy saving.
• Emulgators increase adhesion they effect as an anti-stripping agent
• It can use in four seasons. Especially it gives a chance application in the rainy region and it extends the application period.
• It has a lot of application area and construction methods.
• Bitumen Emulsion does not require petroleum solvent to make them liquid as in cut back and also it is not required to be heated like normal Bitumen. Thus saving imported petroleum oil or firewood.
• Toxic fumes (Hydrocarbon emission) normally emitted from heated bitumen & cutbacks not present when Cationic Bitumen Emulsion is used, as no heating is required for its application.
• Energy saving & control of pollution & safety:
During the last 10-12 yrs., the country was in the quest for alternatives to Hot Mixing technology especially to save our beleaguered environment besides curbing the use of Imported petroleum oil, and our precious forests supplying firewood. Optimum use of Bitumen-emulsions can preserve Petroleum Oil and in turn, save our Environment and Foreign Exchange.s application.
CSS-1 Packing
Packing of bitumen emulsion CSS-1 is in a new thick steel drum on a pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Cationic bitumen emulsion CSS-1 Specifications
Emulsion Type: Slow-Setting
Grade: CSS-1
Standard: ASTM D 2397M – 13
| PropertyProperty | Min | Max | Test Method |
| Test on Emulsions | |||
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 25 °C, SFS | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability test, 24-h, % | – | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Particle charge test | positive | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve test, % | – | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Cement mixing test, % | 2.0 | ASTM D6935 | |
| Distillation: | |||
| Residue, % | 57 | – | ASTM D244 |
| Tests on residue from distillation test: | |||
| Penetration, 25°C (77°F), 100 g, 5 s | 100 | 250 | ASTM D5 |
| Ductility, 25°C (77°F), 5 cm/min, cm | 40 | – | ASTM D113 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene, % | 97.5 | – | ASTM D2042 |
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion CMS-2h
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion CMS-2h Description
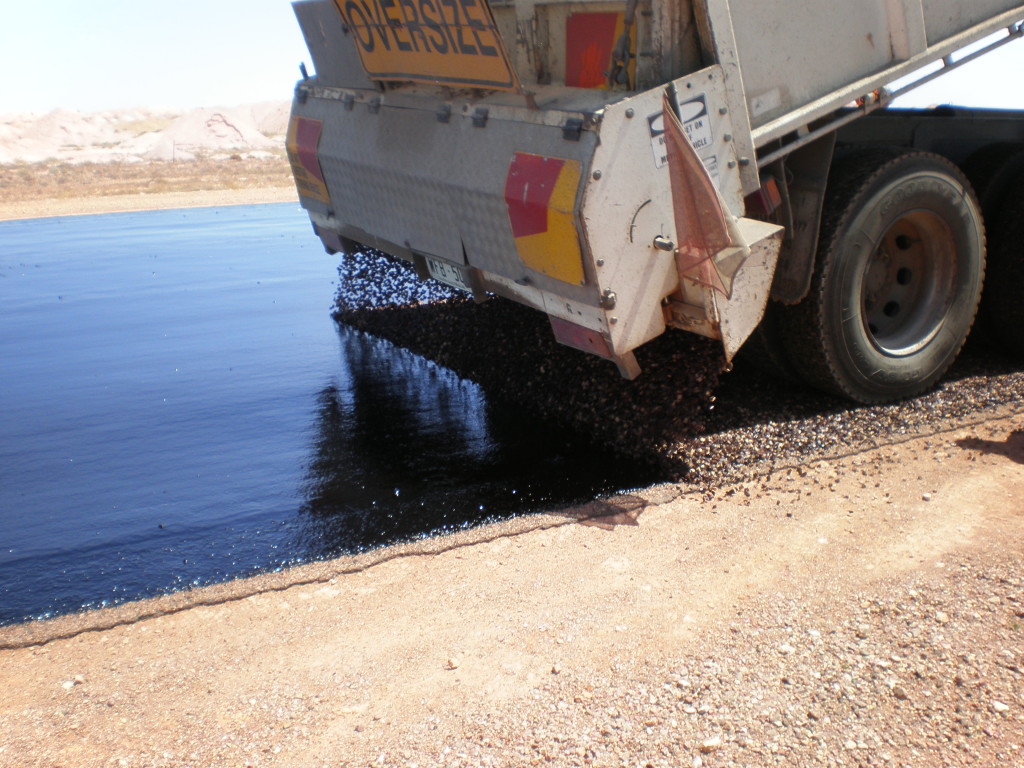

Cationic bitumen emulsions CMS-2h have a positive charge and hence a direct and very rapid reaction between the emulsion and aggregate or pavement is possible. The size of the charge or the Zeta potential affects stability, the larger the charge the greater the repulsion, but as the aggregate is negatively charged the higher the zeta potential the more rapid the reaction.
So it is possible to stabilize a cationic emulsion in the same way that makes it a more rapid break. The other mechanism of evaporation is available too but as the emulsion is stabilized this form of break becomes slower. Thus a balance must be struck. After the electrostatic part of the reaction is complete the emulsion will rely on flocculation and coalescence to complete break.
After the break is completed the water must still be completely evaporated for the residual Asphalt to achieve full strength.
Bitumen emulsion consists of three basic ingredients: bitumen, water, and an emulsifying agent. Based on specifications it may contain other additives, such as stabilizers, coating improvers, anti-strips, or break control agents. It is well known that water and asphalt will not mix, except under carefully controlled conditions using highly specialized equipment and chemical additives.
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion CMS-2h is a cationic emulsion. Bitumen emulsion CMS-2h is usually made by passing the mixture of hot bitumen and water phase between a rotating disc, cone, or wheel and a stator. In the emulsification process, the hot binder is mechanically separated into minute globules and dispersed in water treated with a small quantity of the emulsifying agent. The water is called the continuous phase and the globules of the binder are called the discontinuous phase by proper selection of an emulsifying agent and other manufacturing controls.
Bitumen Emulsion CMS-2h Applications
Cationic emulsions may be used at ambient temperatures with aggregates, which need not be completely dry. Emulsions are less hazardous to use in comparison with the cutback and can be applied in a wider range of conditions. Most CMS-2h applications are listed below:
- Biturubber (Rubber)
- Bitumalch (Malching)
- Prepared cold Mixed Asphalt
- Bituprime (Prime Coat)
- Bitucoat (Fog Seal – Seal Coat)
Successful performance of bitumen emulsions requires selecting the proper type and grade for the intended use. Guidelines presented in this chapter should help select the specific grade and type of emulsion to be used.
The first consideration in picking the right type and grade of the emulsion is how the emulsion will be used. Is it for a planned mix (central or mixed-in-place), a recycled mix, or a prime coat application? Is it for some type of surface application, such as a fog seal, slurry seal, micro-surfacing, or chip seal? Is it for a maintenance mix? Once this decision is made, other project variables must then be considered. Some other factors that affect the selection are:
• Climatic conditions anticipated during construction. The choice of emulsion grade, the design of mix or treatment, and the selection of construction equipment should be dictated by the conditions at the time of construction.
• Aggregate type, gradation, and availability.
• Contractor or construction equipment availability.
• Geographical location. The hauling distance and, in some cases, water availability are important considerations.
the hauling distance and, in some cases, water availability are important considerations.
• Traffic control. Can traffic be detoured or only controlled through the work area?
• Environmental considerations.
• Proper application for pavement preservation or pavement distresses.
• Traffic type and volume.
While general guidelines can be given for selecting emulsions, laboratory testing is strongly recommended. There is no substitute for laboratory evaluation of the emulsion and the aggregate to be used. Different types and quantities of an emulsion should be tried with the aggregate to find the best combination for the intended use. An experienced technician can determine the type and grade of the emulsion to be used.
Cationic emulsions are preferred for use with negatively charged siliceous aggregates such as quartz, granite, sandstone, and river gravel. In general, Cationic emulsions can be used with a wider range of aggregates, will tolerate greater quantities of moisture, and will break at a lower ambient temperature. The main application areas of Emulsion bitumen are surface dressing, tack coats, prime coat, slurry seal, and cold mixing.
Dust control (SS-1, CS-1, CRS-1)
Tack coat (SS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1, CSS-1h, CRS-1)
Prime coat (SS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1, CSS-1h)
Fog seal (SS-1, CSS-1, MS-1-CMS-2, CRS-1)
Penetration prime (SS-1)
Cold mix asphalt, Mulching, Asphalt Sealers (CSS-1)
Chip seal, single, or multiple treatments (RS-1, RS-2, HFMS-1, HFMS-2, HFRS-2, CRS-2, and CRS-2P)
Sand seal (SS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1, CSS-1h, CMS-2s, CRS-1, CRS-2)
Slurry seal (SS-1h, CSS-1h, CSS-1Hp)
Sandwich seal, cape seal, chip seal (CR-2)
Micro surfacing (CQS-1h)
Structural and surface plant mixture (SS-1, SS-1h, HFMS-2s, CSS-1, CSS-1h,)
Stockpiled patching mixture (HFMS-2s, CMS-2s)
In-place road mixing (SS-1, SS-1h, HFMS-2s, HFMS-2, HFMS-2h CMS-2, CMS-2h, CSS-1, CSS-1h)
Crack filler, joint coating (RS-2, HFMS-2h, MS-2, CMS-2h, CRS-2P)
Asphalt sealers, Immediate Maintenance, Stockpile Maintenance Mixes (CMS-2)
Immediate Maintenance (CM2, CM2h)
CMS-2h Advantages
• No petroleum solvent required to liquefy
• Little or no hydrocarbon emissions
•Because of the low viscosity of the Emulsion as compared to hot-applied Bitumen, The Emulsion has good penetration and spreading capacity.
• In most cases, used with no additional heat. It does not need any pre-heating. Thus results in the case of handling for the user, besides saving in cost.
• The ability to coat damp aggregate
• Can use cold materials at remote sites. Cold application of Bitumen Emulsion ensures safety to the workforce; it is a user-friendly product. Being cold-applied the work progresses much faster.
• Wide variety of emulsion types available today
• Economical
• Free from danger ( for fire )
• Environmental
• Harmless for worker health.
• It can use with moisture aggregates. It can be used even with wet aggregates thus enabling users to carry out work during the monsoon also.
• Application temperature is low and does not need heating while storage and transportation period. For this reason, it provides energy saving.
• Emulgators increase adhesion they effect as an anti-stripping agent
• It can use in four seasons. Especially it gives a chance application in the rainy region and it extends the application period.
• It has a lot of application area and construction methods.
• Bitumen Emulsion does not require petroleum solvent to make them liquid as in cut back and also it is not required to be heated like normal Bitumen. Thus saving imported petroleum oil or firewood.
• Toxic fumes (Hydrocarbon emission) normally emitted from heated bitumen & cutbacks not present when Cationic Bitumen Emulsion is used, as no heating is required for its application.
• Energy saving & control of pollution & safety:
During the last 10-12 yrs., the country was in the quest for alternatives to Hot Mixing technology especially to save our beleaguered environment besides curbing the use of Imported petroleum oil, and our precious forests supplying firewood. Optimum use of Bitumen-emulsions can preserve Petroleum Oil and in turn, save our Environment and Foreign Exchange.s application.
CMS-2h Packing
Packing of bitumen emulsion CSS-1 is in a new thick steel drum on a pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Cationic bitumen emulsion CMS-2h Specifications
Emulsion Type: Medium-Setting
Grade: CMS-2h
Standard: ASTM D 2397M – 13
| Property | min | max | Test method |
| Test on emulsions | |||
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 50 °C, SFS | 40 | 450 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability test, 24-h, % | – | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Coating ability and water resistance: | |||
| Coating, dry aggregate | Good | ASTM D244 | |
| Coating, after spraying | Fair | ASTM D244 | |
| Coating, wet aggregate | Fair | ASTM D244 | |
| Coating, after spraying | Fair | ASTM D244 | |
| Particle charge test | Positive | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve test, % | – | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Distillation: | |||
| Oil distillate, by volume of emulsion, % | – | 12 | ASTM D6997 |
| Residue, % | 65 | – | ASTM D244 |
| Tests on residue from distillation test: | |||
| Penetration, 25°C (77°F), 100 g, 5 s | 40 | 90 | ASTM D5 |
| Ductility, 25°C (77°F), 5 cm/min, cm | 40 | – | ASTM D113 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene, % | 97.5 | – | ASTM D2042 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFMS-1
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFMS-1 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFMS-1 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFMS-1 Apllications
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make HFMS-1 an easy to use and a safe product. HFMS-1 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Packing of Bitumen Emulsion HFMS1
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion HFMS-1 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion HFMS1
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 25 °C, SFS | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D6936 | |
| Sieve (%) | — | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 55 | — | ASTM D244 |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | — | ASTM D113 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Float of residue. 60 °C (s) | 1200 | ASTM D139 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFRS-2
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFRS-2 Description
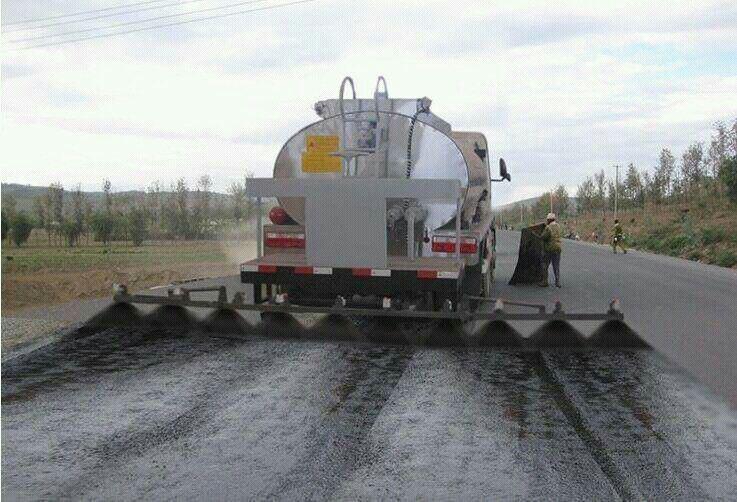

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFRS-2 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFRS-2 Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make HFMS-2 an easy to use and a safe product. HFMS-1 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Packing of Bitumen emulsion HFRS2
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion HFRS-2 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion HFRS2
| PROPERTY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 25 °C, SFS | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | 1 | ASTM D6930 | |
| Demulcibility , 35ml, 8% dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, % | 60 | — | ASTM D6936 |
| Particle charge test | minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 63 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 | |
| Float of residue. 60 °C (s) | 1200 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2h
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2h Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2h has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2h Applications
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make MS-2h an easy to use and a safe product. MS-2h can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2h is recommended for Pre Mix Carpet and Patchwork. The application rate as per MoRTH is as below:

Packing of Bitumen Emulsion MS2h
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion MS-2h is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion MS2h
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 25 °C, SFS | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | 1 | ASTM D6930 | |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Cement mixing (%) | |||
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 65 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 40 | 90 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | ASTM D2042 | |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsions MS-2 Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make MS-2 an easy to use and a safe product. MS-2 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2 is recommended for Pre Mix Carpet and Patchwork. The application rate as per MoRTH is as below:

Packing of Bitumen Emulsion MS2
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion MS-2 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion MS2
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 25 °C, SFS | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve (%) | — | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 65 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | — | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make QS-1h an easy to use and a safe product. QS-1h can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Packing of Bitumen Emulsion QS1h
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion QS-1h is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion QS1h
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SSF , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Viscosity SSF , 50 °C (s) | ASTM D244 | ||
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | ASTM D6930 | ||
| Demulcibility , 0.02 N CaCl2 (%) | |||
| Cement mixing (%) | |||
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 57 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 40 | 90 | ASTM D5 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different braking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsions RS-2 Applications
Anionic Slow Setting bitumen emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make RS-2 an easy to use and a safe product. RS-2 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2 is recommended for Surface Dressing treatment and the application rate as per MoRTH is as below

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS2 Packing
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion RS-2 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Bitumen Emulsion RS2 Specifications
| Properties | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SFS , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | 1 | ASTM D6930 | |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Demulcibility , 35ml, 8% dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, % | 60 | — | ASTM D6936 |
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 63 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different braking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make RS-1 an easy to use and a safe product. RS-1 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
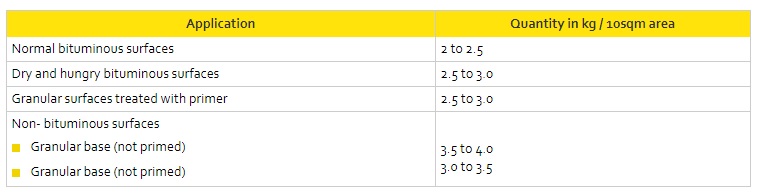
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 is recommended for Tack Coat treatment and the application rates as per MoRTH are as below:
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS1 Packing
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion RS-1 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Bitumen Emulsion RS1 Specification
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SSF , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Demulcibility , 35ml, 8% dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, % | 60 | — | ASTM D6936 |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve (%) | — | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 55 | — | ASTM D244 |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | — | ASTM D113 |
