Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFMS-1
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFMS-1 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFMS-1 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFMS-1 Apllications
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make HFMS-1 an easy to use and a safe product. HFMS-1 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Packing of Bitumen Emulsion HFMS1
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion HFMS-1 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion HFMS1
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 25 °C, SFS | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D6936 | |
| Sieve (%) | — | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 55 | — | ASTM D244 |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | — | ASTM D113 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Float of residue. 60 °C (s) | 1200 | ASTM D139 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFRS-2
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFRS-2 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFRS-2 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion HFRS-2 Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make HFMS-2 an easy to use and a safe product. HFMS-1 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Packing of Bitumen emulsion HFRS2
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion HFRS-2 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion HFRS2
| PROPERTY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 25 °C, SFS | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | 1 | ASTM D6930 | |
| Demulcibility , 35ml, 8% dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, % | 60 | — | ASTM D6936 |
| Particle charge test | minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 63 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 | |
| Float of residue. 60 °C (s) | 1200 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2h
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2h Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2h has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2h Applications
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make MS-2h an easy to use and a safe product. MS-2h can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2h is recommended for Pre Mix Carpet and Patchwork. The application rate as per MoRTH is as below:

Packing of Bitumen Emulsion MS2h
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion MS-2h is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion MS2h
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 25 °C, SFS | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | 1 | ASTM D6930 | |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Cement mixing (%) | |||
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 65 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 40 | 90 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | ASTM D2042 | |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsions MS-2 Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make MS-2 an easy to use and a safe product. MS-2 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion MS-2 is recommended for Pre Mix Carpet and Patchwork. The application rate as per MoRTH is as below:

Packing of Bitumen Emulsion MS2
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion MS-2 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion MS2
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 25 °C, SFS | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve (%) | — | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 65 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | — | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different breaking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion QS-1h Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make QS-1h an easy to use and a safe product. QS-1h can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Packing of Bitumen Emulsion QS1h
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion QS-1h is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Specification of Bitumen Emulsion QS1h
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SSF , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Viscosity SSF , 50 °C (s) | ASTM D244 | ||
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | ASTM D6930 | ||
| Demulcibility , 0.02 N CaCl2 (%) | |||
| Cement mixing (%) | |||
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 57 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 40 | 90 | ASTM D5 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different braking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsions RS-2 Applications
Anionic Slow Setting bitumen emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make RS-2 an easy to use and a safe product. RS-2 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-2 is recommended for Surface Dressing treatment and the application rate as per MoRTH is as below

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS2 Packing
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion RS-2 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Bitumen Emulsion RS2 Specifications
| Properties | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SFS , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | 1 | ASTM D6930 | |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Demulcibility , 35ml, 8% dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, % | 60 | — | ASTM D6936 |
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 63 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 Description

Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different braking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make RS-1 an easy to use and a safe product. RS-1 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
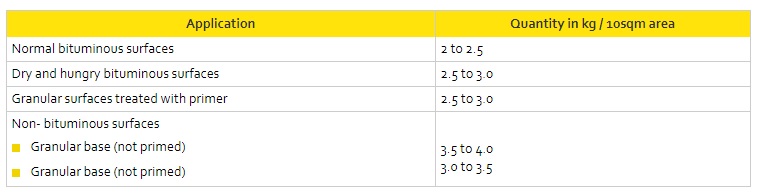
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS-1 is recommended for Tack Coat treatment and the application rates as per MoRTH are as below:
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion RS1 Packing
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion RS-1 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Bitumen Emulsion RS1 Specification
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SSF , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Demulcibility , 35ml, 8% dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, % | 60 | — | ASTM D6936 |
| Particle charge test | Minus | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve (%) | — | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 55 | — | ASTM D244 |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | — | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1h
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1h Description

Anionic Bitumen emulsion SS-1h is a slow-setting, anionic type and is further characterized by their ability to remain stable on storage although produced with equipment that generates a wide range of shearing forces. Such characteristics are imparted to the asphalt emulsions through the use of emulsion-conditioner compositions comprising a partially desulfonated lignosulfonate, preferably an anionic or nonionic emulsifying agent and, optionally, a thickener.
For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different braking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
An Anionic emulsion has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
Usage of anionic bitumen emulsion SS-1h is two phases of water and bitumen which are not possible to mix and the first interphase is inside of the outer phase. The particle size of the emulsion is 0.1 to 5 micron. In normal conditions and without emulsifier the two parts of emulsion SS1 are unstable and quickly will segregate. By adding emulsifier into water and bitumen that is the alkaline salt with Ammonium Salt in the high-speed mixer at ISO condition making bitumen SS-1h.
The percentage of emulsifiers is 3-5% and total water content is between 30-50%. By adding an Emulsifier to bitumen and water we put anionic electron on the material and each particle of bitumen became like a circle with a size of 0.001 to 0.01 mm and become floating in the water. Using bitumen SS1 is environmentally friendly since any flammable material or kerosene is not used and firing of the bitumen during the usage would be zero.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1h Application
Anionic Slow Setting Bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-fibered liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make SS-1h an easy to use and a safe product. SS-1h can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
Anionic Bitumen emulsion SS1h Packing
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion SS-1h is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Bitumen Emulsion SS1h Specifications
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SSF , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Viscosity SSF , 50 °C (s) | — | — | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Demulcibility , 0.02 N CaCl2 (%) | |||
| Cement mixing (%) | 2 | ||
| Sieve (%) | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Residue by distillation (%) | 57 | ASTM D244 | |
| Residue penetration, 25 °C | 40 | 90 | ASTM D5 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | — | ASTM D2042 |
| Residue ductility, 25 °C, 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1 Description

For anionic and emulsions, there are several grades of different braking characteristics. Rapid-setting emulsions are used for surface dressing, while medium or slow-setting emulsions are used for ‘mixtures’, that is mixed with aggregate either in concrete-type mixers or in situ. Rapid-setting emulsions are not used for mixtures because they would tend to set during the mixing process and clog the mixer. Generally, in making mixtures, the finer the aggregate used, the slower setting the emulsion that has to be used. Therefore, stone mixtures require medium-setting emulsions and sand mixtures require a slow-breaking emulsion. With anionic emulsions, the breaking process is predominantly by evaporation of the water in the emulsion continuous phase. Because of this, anionic emulsions are susceptible to temperature and humidity in terms of their breaking properties.
An Anionic emulsion has a negative charge, most of the things in the world are Anionic and that is why the majority of Research and Development, formulating, and lab testing has been done in the Industrial Coatings Industry to make coatings from Anionic systems. When an Anionic emulsion is mixed with a Cationic emulsion a strong bond develops and the result is the changing of the substance to a solid. This result is not ideal to be used as a coating because it cannot be applied to substrates.
Anionic Bitumen emulsion SS-1 is a slow-setting, anionic type and is further characterized by their ability to remain stable on storage although produced with equipment that generates a wide range of shearing forces. Such characteristics are imparted to the asphalt emulsions through the use of emulsion-conditioner compositions comprising a partially desulfonated lignosulfonate, preferably an anionic or nonionic emulsifying agent and, optionally, a thickener.
Usage of anionic bitumen emulsion SS-1 is two phases of water and bitumen which are not possible to mix and the first interphase is inside of the outer phase. The particle size of the emulsion is 0.1 to 5 micron. In normal conditions and without emulsifier the two parts of emulsion SS1 are unstable and quickly will segregate. By adding emulsifier into water and bitumen that is the alkaline salt with Ammonium Salt in the high-speed mixer at ISO condition making bitumen SS1.
The percentage of emulsifiers is 3-5% and total water content is between 30-50%. By adding an Emulsifier to bitumen and water we put anionic electron on the material and each particle of bitumen became like a circle with a size of 0.001 to 0.01 mm and become floating in the water. Using bitumen SS1 is environmentally friendly since any flammable material or kerosene is not used and firing of the bitumen during the usage would be zero.
This kind of anionic bitumen has more adhesive to building material which contains lime.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1 Applications
Anionic Slow Setting bitumen Emulsion is the cold/non-liberated liquid applied waterproofing bitumen emulsion. The product is made using a process in which the bitumen, special emulsifier, water, and other additive have been gone through a high shear rate colloid mill and the properties of bitumen have a direct effect on the emulsion specification. This product has been specifically developed to provide waterproofing and building application, concrete, and metal surface. The high flash point and the low solvent content make SS-1 an easy to use and a safe product. SS-1 can be applied by using a painting brush, squeegee, airless spray, and roller.
It is using for cold asphalt in cold or humid or sealing. Asphalt emulsions are widely used in highway construction, surfacing, and maintenance. They are also used in various other applications where water-repellent surfaces are needed. Slow-setting emulsions are grades of emulsions that are sufficiently stable to allow mixing with fine or dusty aggregate mineral particles and further processing before setting to a coherent mass. Such grades of asphalt emulsions (bitumen SS-1 grade), when anionic, react chemically with portland cement constituents forming a water-insoluble salt and thus possess valuable water-resistant characteristics.
Anionic Bitumen Emulsion SS-1 Packing
Packing of anionic bitumen emulsion SS-1 is in the new thick steel drum on the pallet to prevent any leak inside of container also bulk in bitutainer and tanker.
Bitumen Anionic Emulsion SS-1 Specifications
| PROPETRY | MIN | MAX | TEST METHOD |
| Viscosity SSF , 25 °C (s) | 20 | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Viscosity SSF , 50 °C (s) | — | — | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability, 24h (%) | — | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Demulcibility , 0.02 N CaCl2 (%) | — | — | |
| Cement mixing (%) | — | 2 | |
| Sieve (%) | — | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Residue (%) | 57 | — | ASTM-D244 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene % | 97.5 | ASTM D2042 | |
| Penetration 77°F (25°C) 100g,5s mm | 100 | 200 | ASTM D5 |
| ductility, 77°F (25 °C), 5cm/min (cm) | 40 | ASTM D113 |
